Gummy Candy
Background
Gummy candy is a unique candy composed of gelatin, sweeteners, flavorings, and colorings. Because of its nature it can be molded into literally thousands of shapes, making it one of the most versatile confection products ever. First developed in Germany in the early 1900s, it gained great popularity in the United States during the 1980s. Today, it continues to be popular, with sales totaling over $135 million in 1996 in the United States alone.
History
Gummy candy represents a more recent advance in candy technology. The technology, derived from early pectin and starch formulations, was first developed in Germany in the early l900s by a man named Hans Riegel. He began the Haribo company, which made the first gummy bears in the 1920s. While gummy candy has been manufactured since this time, it had limited worldwide distribution until the early 1980s. It was then when Haribo began manufacturing gummy bears in the United States. The fad caught on, causing other companies to develop similar products. The gummy bears led to other types of gummy candy entries from companies such as Hershey, Brach's, and Farley's. Now, the candy is available in various different forms, from dinosaurs to fruit rolls. According to one gelatin manufacturer, nearly half of all gelatin made worldwide currently goes to making gummy candies.
Raw Materials
Gummy candy recipes are typically developed by experienced food technologists and chemists. By blending together different ingredients, they can control the various characteristics of gummy candy, such as texture, taste, and appearance. The primary ingredients include water, gelatin, sweeteners, flavors, and colors.
The main ingredient responsible for the candy's unique, gummy characteristics is gelatin. This is a protein derived from animal tissue that forms thick solutions or gels when placed in water. When used at an appropriate concentration, the gels take on the texture of the chewy, gummy candy. However, since these gels are thermoreversible, which means they get thinner as they are heated, gummy candies have a "melt in the mouth" characteristic. Both the texture and the amount of time it takes the candy to dissolve in the mouth can be controlled by the amount of gelatin used in a recipe.
Since gelatin is a tasteless and odorless compound that contains no fat, sweeteners and flavorings are added to give gummy candy its taste. Various sugars are added as sweeteners. Sucrose, derived from beets or sugar cane, provides a high degree of sweetness to the gummy candy. Fructose, which is significantly sweeter than common sucrose, is another sugar that is often used. Corn syrup is also used because it helps prevent the other sugars from crystallizing and ruining the gummy texture. Also, corn syrup helps add body to the candy, maintain moisture, and keep costs lower. Another sweetener is sorbitol, which has the added benefit of helping the candy maintain its moisture content. In addition to flavor, some of these sweeteners have the added benefit of preserving the gummy candy from microbial growth.
The sweetness of gummy candy is only one of its characteristics. Artificial and natural flavors are also used to create a unique taste. Natural flavors are obtained from fruits, berries, honey, molasses, and maple sugar. The impact of these flavors can be improved by the addition of artificial flavors that are mixtures of aromatic chemicals and include materials such as methyl anthranilate and ethyl caproate. Also, acids such as citric acid, lactic acid, and malic acid are added to provide flavor.
Gelatin gels have a natural faint yellow color, so dyes are added to create the wide array of colors found in gummy candy. Typical dyes include Red dye #40, Yellow dye #5, Yellow dye #6, and Blue dye #1. Using these federally regulated dyes, gummy manufacturers can make the candy almost any color they desire.
The textural characteristics of gelatin gels depends on many factors, such as temperature, method of manufacture, and pH. While the manufacturing method and temperature can be physically controlled, the pH is controlled chemically by the addition of acids. These include food grade acids such as citric acid, lactic acid, fumaric acid, and malic acid. Other ingredients are added during the manufacturing process as flavorants, lubricating agents, and shine enhancing agents. These include materials like beeswax, coconut oil, carnauba wax, mineral oil, partially hydrogenated soybean oil, pear concentrate, and confectioner's glaze, which are often added during the filling phase of manufacture.
The Manufacturing
Process
Gummy manufacturing uses a starch molding process. First the candy is made, then it is filled into starched lined trays. The filled trays are then cooled overmight and the resulting formed candy is emptied from the trays. In the mass production of gummy candy, significant improvements have been made to increase the speed and efficiency of this process.
Compounding
- 1 The manufacture of gummy candy begins with compounding. Factory workers, known as compounders, follow instructions outlined in the recipes and physically pour the appropriate amount of gummy raw materials into the main mixing tanks. These tanks, which are equipped with mixing, heating, and cooling capabilities, are quite large. Depending on the size of the batch, gummy candy compounding can take from one to three hours. When the batch is complete, it is sent to the Quality Control (QC) laboratory to make sure that it meets the required specifications.
Forming candy
- 2 After the gummy candy is compounded and passes QC testing, it is either pumped or transferred to a starch molding machine known as a Mogul. This machine can automatically perform the multiple tasks involved in making gummy candy. It is called a starch molding machine because starch is a main component. In this machine, starch has three primary purposes. First, it prevents the candy from sticking to the candy molds, which allows for easy removal and handling. Second, it holds the gummy candy in place during the drying, cooling, and setting processes. Finally, it absorbs moisture from the candies, giving them the proper texture.
- 3 Making gummy candy in a Mogul is a continuous process. At the start of the machine, trays that contain previously filled, cooled, and formed gummy candy are stacked. The trays are then removed from the stack one-by-one and iwove along a conveyor belt into the next section of the machine, known as the starch buck.
-
4 As they enter the starch buck, the trays are inverted and the gummy
candy falls out into a vibrating metal screen known as a sieve. The
vibrating action of the sieve, in concert with oscillating brushes,
removes all of the excess starch that adheres to the gummy candy. These
pieces then move along a conveyor belt to trays, where they are manually
transferred to other machines by which they can be decorated further and
placed into appropriate packaging. A more recent advance, called the
pneumatic starch buck, further automates this step. In this device, a
tightly fitting cover is placed over the filled trays. When it is
inverted, the candies adhere to the cover and remain in their
ordered position. The excess starch is then removed by fast-rotating compressed-air jets. The candy can then be conveyed for further processing.
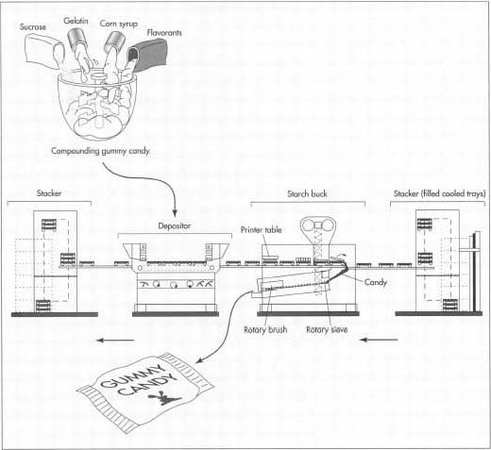 Gummy candy is manufactured in a machine called a Mogul. Cooled trays of gummy candy are inverted in the starch buck. This candy is ready for packaging. The trays are then filled with starch to keep the candy from sticking and sent to the printer table, which imprints a pattern into the starch. The depositor fills the trays with the hot candy mixture, and the trays are sent back to the stacker to cool for 24 hours. Then the machine can start the process again.
Gummy candy is manufactured in a machine called a Mogul. Cooled trays of gummy candy are inverted in the starch buck. This candy is ready for packaging. The trays are then filled with starch to keep the candy from sticking and sent to the printer table, which imprints a pattern into the starch. The depositor fills the trays with the hot candy mixture, and the trays are sent back to the stacker to cool for 24 hours. Then the machine can start the process again. - 5 The starch that is removed from the gummy candy is reused in the process, but first it must be cleaned, dried, and otherwise reconditioned. Candy particles are first removed by passing the starch through a metal screen known as a sieve. It is then conveyed to a recirculating starch conditioning system. As it enters this machine, it is dried by being passed through hot, moving air. After drying, the starch is cooled by cool air jets and conveyed back out to the Mogul to be reused in the starch molding process.
- 6 The starch returns from the drier via a conveyor belt to the Mogul, where it is filled into the empty trays and leveled. These were the same trays that were inverted and emptied in step two. These starch-filled trays then move to a printer table. Here, a board that has the inverse of the mold printed on it presses the starch down so the mold has an indent in it. From here, the trays are moved to the depositors.
- 7 The gummy candy, compounded in step 1, is transferred to the depositors. This is the part of the mogul that has a filling nozzle and can deliver the exact amount of candy needed into the trays as they pass under it. The depositor section of the mogul can contain 30 or more depositors, depending on how many imprints there are on the trays. In more modern depositors, the color, flavor, and acids can be added to the gummy base right in the depositor. This allows different colors and flavors to be made simultaneously, speeding up the process.
- 8 The filled trays are moved along to a stacking machine and then sent to a cooling room, where they stay until they are appropriately cooled and formed. This part of the process can take over 24 hours. After this happens, the trays are moved back to the Mogul, and the process starts all over again.
Quality Control
Quality control begins with the evaluation of the incoming raw materials. Before they are used, these ingredients are tested in the QC lab to ensure they conform to specifications. Various sensory characteristics are checked, including appearance, color, odor, and flavor. Many other characteristics, such as the particle size of the solids, viscosity of oils, and pH of liquids, are also studied. Each manufacturer depends on these tests to certify that the ingredients will produce a consistent, quality batch of gummy candy.
The characteristics of each batch of final product is also carefully monitored. Quality control chemists and technicians check physical aspects of the candy that include appearance, flavor, texture, and odor. The usual method of testing is to compare them to an established standard. For example, the color of a random sample is compared to a standard set during product development. Other qualities such as taste, texture, and odor are evaluated by sensory panels. These are made up of a group of people who are specially trained to notice small differences. In addition to sensory tests, many instrumental tests that have been developed by the industry over the years are also used to complement tests performed by humans.
The Future
Increasing the safety, speed, and efficiency of the manufacturing process are the major improvements being investigated for the future of the gummy candy industry. In any starch molding process, safety is a major concern because starch dryers represent an explosion hazard. Currently the U.S. government recommends minimizing these hazards by using spark-proof switches, blast walls, and other such mechanisms. Newer starch drying machines represent a reduced explosion hazard and improved microbiological killing. Additionally, moguls are being constructed that operate faster and more efficiently.
Since new products are the lifeline of any company in the candy business, new gummy flavors and colors are constantly being added to the base formula. Also, unique shapes are being molded, creating a plethora of new gummy candy. New forms of gummy candy are also being developed, most recently, a combination of gummy candy and marshmallow.
Where to Learn More
Books
Traxler, Hans. The Life and Times Of Gummy Bears. Harper Collins, 1993.
Periodicals
Gelatin. Gelatin Manufacturers Institute of America, Inc., 1993.
Lepree, Joy. "Gelatin market softening off-set by feedstock crimp." Chemical Marketing Reporter, July 18, 1994, p. 16.
Tiffany, Susan. "Infant Gummi Bear takes giant steps." Candy Industry, January 1995, p. 44.
— Perry Romanowski
my question is...is it right as i heard that the gelatin is primary made of foam extracted from boild Pork bones?
best regards.
Zaher Tbele.